Aromaticity explain by Hückel's Rule and Craig's Rule for UGC CSIR-NET GATE IIT JAM TIFR DRDO BARC Chemistry.
Application of Aromatic, Nonaromatic, Antiaromatic, Homoaromaticity & Quasi-aromatic compounds for competitive examination.
Application of Aromaticity with PDF file.
Basic Concepts
of Aromaticity //
📚 PDF File also available 👉👉 Click Here
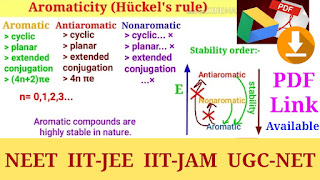
Order Stability and Resonance Energy:- Aromatic > Homoaromatic > Antiaromatic > Nonaromatic








🎦 For watch these videos for 👉👉 Full Concepts
Application of Aromatic, Nonaromatic, Antiaromatic, Homoaromaticity & Quasi-aromatic compounds for competitive examination.
Application of Aromaticity with PDF file.
Basic Concepts
of Aromaticity //
Aromatic, Nonaromatic, Antiaromatic compounds.
Quasi-aromatic & homoaromaticity.
Quasi-aromatic & homoaromaticity.
Aromaticity Based on Hückel's Rule.
Application of Aromaticity.
🎦 Aromaticity 👉 Part 1
🎦 Aromaticity 👉 Part 2
📚 PDF File also available 👉👉 Click Here
Order Stability and Resonance Energy:- Aromatic > Homoaromatic > Antiaromatic > Nonaromatic
〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️
〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️〰️
Aromaticity:- in Organic Chemistry, the Aromaticity is a property of Cyclic, planar structure with a ring of resonance bonds that gives the increased stability compared to other geometric with the same set of atoms. Aromatic compounds are very stable, and they do not break apart easily to react with other compounds.
Antiaromatic:- it is also a Cyclic molecule with a pi-electron system but there has higher energy due to the presence of 4n delocalized electrons in it. And Antiaromatic compounds are highly unstable and highly reactive in nature.
Nonaromatic:- nonaromatic are every other molecules that fails one of these conditions (i.e., Cyclic, planar, conjugation and 4n or (4n+2) number of delocalized electrons, so anyone of these conditions is not fulfill, then the molecule is called non Aromatic compound).
Quasi-aromatic:- Quasi-aromatic compounds are those in which the charges are present on the ring/molecule, and they take a part of Aromaticity of the compound.
Homoaromaticity:- in Organic Chemistry, it refers to a special type of Aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp³ hybridized carbon atom.
Antiaromatic:- it is also a Cyclic molecule with a pi-electron system but there has higher energy due to the presence of 4n delocalized electrons in it. And Antiaromatic compounds are highly unstable and highly reactive in nature.
Nonaromatic:- nonaromatic are every other molecules that fails one of these conditions (i.e., Cyclic, planar, conjugation and 4n or (4n+2) number of delocalized electrons, so anyone of these conditions is not fulfill, then the molecule is called non Aromatic compound).
Note:- "All Quasi-aromatic compounds are aromatic but all aromatic compounds are not Quasi-aromatic compounds"
Quasi-aromatic:- Quasi-aromatic compounds are those in which the charges are present on the ring/molecule, and they take a part of Aromaticity of the compound.
Homoaromaticity:- in Organic Chemistry, it refers to a special type of Aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp³ hybridized carbon atom.








🎦 For watch these videos for 👉👉 Full Concepts
Hückel's Rule for Aromaticity:- In 1931, German chemist and physicist Erich Hückel proposed a theory to determine if a planar ring molecule would have Aromatic properties. His rule states that if a Cyclic, planar molecules has (4n+2) number of π electrons, then it is considered as an Aromatic compound. This rule come to be known as Hückel's Rule for Aromaticity.
Four Criteria for Aromaticity:- When we deciding a compound is Aromatic, then go through the following criteria. If the compound doesn't meet all the following four criteria , then it is called not Aromatic compound.
1. The molecule should be Cyclic.
2. The molecule should be planar.
3. The molecule should be maintain conjugation.
4. The molecule has (4n+2)π number of electrons. (n= 0, 1,2,3....)
📚✔️ In the given molecule Pyrene , the π bond shown in green is in cross conjugation (shown in green in figure 1). This bond( figure 2) is excluded from interaction with rest of conjugated system. Hence , the central C=C isn't hosted by the largest p orbital loop, so it's not counted towards Hückel's rule for aromaticity.
The outer periphery (shown in blue in figure 3), is a loop of 14π electrons , therefore aromatic. This may be possible hückel double bond you are referring to.
The π bond in cross-conjugation (shown in green) maybe non-hückel double bond.
Four Criteria for Aromaticity:- When we deciding a compound is Aromatic, then go through the following criteria. If the compound doesn't meet all the following four criteria , then it is called not Aromatic compound.
1. The molecule should be Cyclic.
2. The molecule should be planar.
3. The molecule should be maintain conjugation.
4. The molecule has (4n+2)π number of electrons. (n= 0, 1,2,3....)
📚✔️ In the given molecule Pyrene , the π bond shown in green is in cross conjugation (shown in green in figure 1). This bond( figure 2) is excluded from interaction with rest of conjugated system. Hence , the central C=C isn't hosted by the largest p orbital loop, so it's not counted towards Hückel's rule for aromaticity.
The outer periphery (shown in blue in figure 3), is a loop of 14π electrons , therefore aromatic. This may be possible hückel double bond you are referring to.
The π bond in cross-conjugation (shown in green) maybe non-hückel double bond.